Table of Contents
Creating a Superstructure
Overview
In this section of the Railtool documentation, we explain the fundamentals required to create railway tracks in SubwaySim 2.
A central and essential part of track construction is the so-called Superstructure. The Superstructure is a data asset that contains all important information required to build tracks, such as geometry, materials, rail profiles, and additional infrastructure data.
Without a Superstructure, the Railtool cannot create usable track segments.
Creating a Superstructure
To make it as easy as possible for users to get started, we recommend using an existing Superstructure that is already included in the Modding SDK.
For advanced users who want to understand how a Superstructure is created from scratch, the following steps explain the manual process.
Creating a New Superstructure Asset
First, create the required folder structure inside your plugin.
In your plugin content directory:
- Create a folder named Infrastructure
- Inside it, create another folder named Superstructures
Once you are inside the Superstructures folder:
- Right-click in the Content Drawer
- Select Data Asset

In the class selection window:
- Search for Super Structure Data Asset
- Select it and confirm

After creating the asset, name the Superstructure freely. We recommend choosing a name that reflects the type of track construction it represents.
Ready-to-Use Superstructures
Several preconfigured and ready-to-use Superstructures are already included in the SDK.
They can be found under:
`SubwaySim2_Modding / RailwaySystem / Superstructures`
Please note:
- These Superstructures do not include power rails
- They are mainly intended as examples or templates
Migrating an Existing Superstructure
For most use cases, we recommend migrating an existing Superstructure from the sample content.
The default sample Superstructure is located at:
`Simuverse_SampleModMap / Infrastructure / RailwaySystem / DataAssets`
The asset is named:
`DL_SampleMapDefault`
The migration process works exactly as described in: Migrating Assets into a User Plugin
Important
When migrating the Superstructure:
- Only migrate assets from `Simuverse_SampleModMap`
- Do NOT migrate assets from `SubwaySim2_Modding`

Migrating from the wrong plugin can cause dependency issues and errors in your mod.
Result After Migration
After a successful migration, the Superstructure and all required dependencies will be located under:
`SubwaySim_SDK_Testplugin / Infrastructure / RailwaySystem / DataAssets`
At this point, the Superstructure is available inside your plugin and ready to be used with the Railtool.
Using Custom Meshes for Superstructures
If you want to use custom meshes for your Superstructure (for example rails, clamps, sleepers, or ballast), it is highly recommended to base them on existing assets from the SDK.
To do this, you can export the original meshes from Unreal Engine back into FBX format and use them as reference in your 3D software (e.g. Blender).
This helps ensure:
- Correct origin placement
- Proper scale and orientation
- Compatibility with the Railtool and Superstructure system
A detailed guide on how to export Unreal assets can be found here:
Using reference meshes greatly reduces alignment issues and avoids unexpected behavior when assigning custom assets to a Superstructure Data Asset.
Superstructure Contents
In this section, we explain how a Superstructure Data Asset is structured and which information it contains.
The Superstructure defines all fundamental properties required by the Railtool to generate tracks correctly. It controls the visual appearance, physical layout, and functional behavior of the railway infrastructure.
The Data Asset is divided into three main sections:
- Base Settings
- Switches
- Third Rail
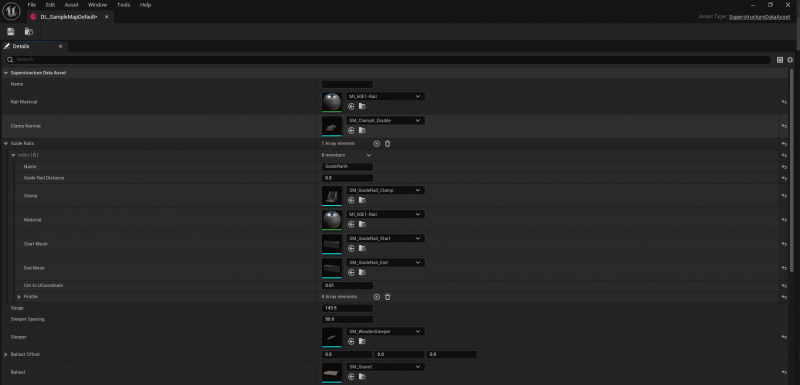
Base Settings
The Base Settings section contains all fundamental information required to create standard track segments.
Base Settings Overview
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Rail Material | Material applied to the rails and visible track geometry. |
| Clamp Normal | Static Mesh used for standard rail clamps. |
| Guide Rails | Additional guiding rails for special track sections. |
| Gauge | Distance between the rails. |
| Sleeper Spacing | Distance between individual sleepers. |
| Sleeper | Static Mesh used for sleepers. |
| Ballast Offset | XYZ offset applied to the ballast mesh. |
| Ballast | Static Mesh used for the ballast bed. |
Rail Material
Defines the material applied to the rail geometry.
Clamp Normal
Specifies the Static Mesh used for standard rail clamps.
Guide Rails
Guide Rails are additional rail elements used in:
- Switches
- Tight curves
- Special track sections
They are also known as:
- Guard Rails
- Guide Rails
- Zwangsschienen / Führungsschienen
Guide Rail Data Layer
Guide Rails are defined using a Data Layer Asset.
Guide Rail Parameters
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the Data Layer asset. |
| Guide Rail Distance | Distance from the standard rail. |
| Clamp | Holder mesh for the guide rail. |
| Material | Material applied to the guide rail. |
| Start Mesh | Mesh at the beginning of the guide rail. |
| End Mesh | Mesh at the end of the guide rail. |
| Cm to UCoordinate | Conversion factor for UV mapping. |
| Profile | Procedural cross-section definition. |
Guide Rail Profile
The profile defines the procedural geometry of the guide rail.
Important Notes
- All distances are defined in Unreal Units (cm)
- Incorrect profiles may cause visual or collision issues
Gauge
Defines the track gauge.
Standard gauge:
- 1435 mm
- 143.5 cm (Unreal Units)
Sleeper Spacing
Defines the distance between sleepers along the track.
Sleeper
Defines the Static Mesh used for sleepers.
Ballast Offset
Defines the XYZ offset of the ballast mesh.
Ballast
Defines the Static Mesh used for the ballast bed.
Switches
The Switches section defines meshes and parameters for automatically generated turnouts.
Switches Overview
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Switch Guard Dist | Guide rail distance at switch exit. |
| Clamp Mini Inner | Small clamp at switch start. |
| Clamp Blade | Clamp for switch blades. |
| Clamp Guard | Clamp for rails with guide rail. |
| Clamp Single Inner Half | Inner single clamp. |
| Clamp Single Outer Half | Outer single clamp. |
| Hollow Sleeper | Sleeper with internal linkage. |
| Switch Motor | Motor mesh. |
| Manual Switch Lever | Blueprint for manual switches. |
| Switch Blade Throw Bar | Blade linkage. |
| Clearance Marker Mesh | Clearance marker mesh. |
Third Rail
The Third Rail section defines the power rail system for electric vehicles.
If no Third Rail Data Layer is present, vehicles will display:
“No Power”
Third Rail Overview
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Third Rail Begin | Start mesh. |
| Third Rail Mid | Looping mesh. |
| Third Rail End | End mesh. |
| Third Rail Mount | Holder mesh. |
| Third Rail Offset | XYZ offset. |
Important Notes
- Third Rail Data Layers are required for powered tracks
- Incorrect offsets can lead to power loss or misalignment
Next Step
With the Superstructure configured, all fundamental data required for track generation is now available.
In the next chapter, you will learn how to use the Railtool to actually place tracks, create curves, switches, and define railway layouts on your map.